What Types of computer?Classified of computer
Types of computer
Computer can be classified through deferment ways. They can be classified on the basis of the way they process data according data, according to their size and model, etc. it is found that many writers have classified computer into Microcomputer, Minicomputer, Workstation, Mainframe & Supercomputer in term of their size but all of these are the types of digital computer so it is better to study them the topic "Type of Digital Computers".
Here we'll classify computer in terms of the way the computer process data. According to the way they process data, computer can be broadly classified into their groups. They are:
1. Digital computer
2. Analog computer
3. Hybrid computer
1. Digital computer
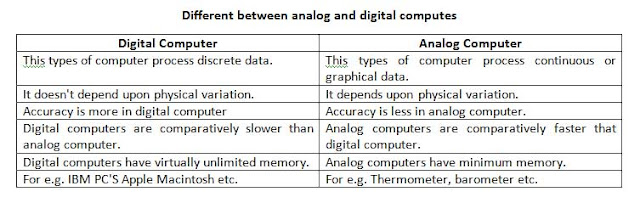
The computer that process discreet data in binary form (i.e. 1&0) is known as digital computer. It required some entity to represent numbers. The representations is not a simple one-to-one relationship, but is deterred by a kind of algorithm called the binary number systems, this algorithm transforms a number/ character into a sequence of 0's and 1's internally in the machine (computer).
The accuracy of digital computer I only limited by the size of registers (to be discussed later) and memory. Letters and works are also coded in binary form. Digital computers have almost an unlimited memory and potentially a much higher accuracy, as it doesn't depend on physical quantities for processing.
2. Analog computer
The computer that process continuous date (value/ quantities) is known as analog computer. Computations are carried out with physical quantities such as voltage, current, air pressure, liner distance, temperature; velocities of rotating shift etc. analog computer utilizes some sorts of analogue or analogy, such as Ohm's Law, to affect a solution, and are used most often as controlling device in some continuous process. Since, analog computers use some physical analogue for representing numbers; they can often avoid much time-consuming arithmetic. However, it cannot perform logical operations, it has minimal memory, setting a problem is arduous and even the most sophisticated of them is limited in problem it can accept, furthermore, analog computer can never be extremely accurate, since quantities are always difficult to measure precisely and tend to fluctuate somewhat with change in temperature, humidity, degree of wear, and so on.
3. Hybrid computer
The computer that is especially designed by combining the best features of analog and digital computers is called Hybrid Computer. This computer use both digital and analog Components to process continuous as well discrete (digital data). It can convert data from analog to digital and vice versa with the help of analog to digital converter (ADC) and digital to analog converter (DAC). This computer has speed of analog and accuracy of digital. The use of Hybrid computers has been restricted to the specialized applications like weather forecasting. Hospitals etc. in hospitals, analog part of hybrid computer is responsible for measurement of patient's heartbeat, blood pressure, temperature and other vital signs and them operations is carried out in digital fashion to monitor patient's vital signs.
Different between analog and digital computes
Types of digital computers
Digital computers can be classified according to their physical size, speed, processing capacities memory size, disk storage capacities, cost, application areas etc. the various classes of digital computers are explained below:
1. microcomputer
The computer that is based on microchips (microprocessor) such as Intel 8386, 80846 etc is known as microcomputer. It is also known as personal computer or home computer. The word size of microcomputer is 8 to 12 bits. Microcomputer is generally single processor, single user system designed for performing basis operations like education, training, small business applications etc.
It is smaller than microcomputer. IBM PC'S IBM Compatibles, Apple Macintosh etc are its examples.
2. minicomputer
Minicomputer is larger than microcomputer and smaller than mainframe. It is more powerful than microcomputer in terms of processing power and storage capacities. The computer is modified from single user concepts of microcomputer to multi-user concept. The word size is 32 bits or more. It is useful for small business organizations and real-time applications such as processing control system.
IBM 4384, CDC-600, CYBER 170 are its examples.
Furthermore, the new design advancement is computer has evolve and and this advancement in computer is known as Ultra Computer. This advancement will be the new generation of computer.
Characteristics of computers
Irrespective of types and size, all computers have common characteristics. The common characteristics of computer are as follows.
a. speed
Computer can process at extremely fats rate at MIPS (Million Instructions per second). A computer can operate at speed measured in nanoseconds and even in Pico seconds.
The following terms are used to describe the processing capacities.
Millisecond = 10-3 of a second
Microsecond = 10-6 of a second
Nanosecond = 10-9 of a second
Pico second = 10-12 second
b. storage
A computer can store a large amount of data. With more and more auxiliary storages devices, which are capacities of storing huge amount of data. The storage capacity of computer is virtually unlimited. The capacity of secondary memory ranges from 540 MB to multiple of Gigabytes (GB).
c. accuracy
The accuracy of a computer is very high. Errors in computer are often due to human factors rather than the technological flaws. Errors in computer occur if and only if a program is wrongly coded or the data is corrupted or if the program logic is flawed or data is entered wrongly.
d. diligence
Diligence means being constant and earnest in effort and application. Human beings suffer from weakness like tiredness, lacks of concentration etc. humans have feelings, they become sad, depressed, bored and negligent and it will reflect on the work they do. Computer can care all these inabilities of the human begins, as it will not get depressed or losses concentration.
e. versatility
Computers are very versatile machine. They are capable of performing almost any task, provided the task can be reduced to a series of logical steps. They can communication with other computers and can receive and send data in various forms like text, sound, graphics, video etc.
f. automation
The level of automation achieved in a computer is phenomenal. It is not a simple calculator where you have to punch in the number and press the 'equal to ' sign to get the result. One the task is initiated computers can proceed on its own till its completion.
g. reliability
Computer became essential equipment in normal people's day-to day work. The possibility of using the versatile range of devices and durability, its popularity is increasing day by day. Every one performs to use computers as it has more capabilities and it became a reliable machine.
Computer applications(what is Computer Applications)
The computer is truly amazing machine. Today, computers are either directly or indirectly influencing almost every aspect of our lives. Here we'll explain the major application areas of computers.
a. business
In business, computers are used for variety of purposes ranging from decision making to electronic commerce. It is also used to control stock of raw materials and finished product, send bills to customers, calculate employee pay and taxes etc.
b. medicine and health care
Computers are extensively used in medicine. It is used for diagnosing illnesses; monitor the conditions of patients and keeping the necessary records. Many innovative medical application use small, special-purpose computers. For example, pacemakers are computer that operate within the human body help to maintain heartbeat.
At laboratory, computers perform tests such as X-RAY, CT-SCAN etc.
c. education
Computers have brought revolution in the field of education. Now, student, teachers and many others use computers in school and colleges. People use computers in the library to read magazines and journals from the computer terminal rather than searching the shelves for paper originals. Teachers use computer as a presentation tool, to explain difficult topics more clearly and easily to their students use computers to develop their science project, do their mathematical problems.
Student to improve their knowledge of any subject use Computer Assisted Learning (CAL).